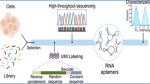
Aptamers are short strands of RNA or DNA that can bind to specific targets, such as proteins or cells. They are valuable tools in various fields, including cell imaging, drug delivery, and therapeutics. Among these, RNA aptamers stand out due to their unique characteristics. They exhibit complex structural diversity and flexibility, which allows them to bind with high affinity and specificity to their targets. This flexibility also makes them easier to chemically modify compared to DNA aptamers, broadening their potential applications in research and medicine.
The Challenge of Selecting RNA Aptamers
Despite their advantages, traditional methods for selecting RNA aptamers can be time-consuming and labor-intensive. These methods often require numerous rounds of screening to find the aptamers that effectively bind to the desired target. This lengthy process can limit the widespread application of RNA aptamers in research and clinical settings, making it essential to develop more efficient selection techniques.
Introducing ID-SELEX: A Streamlined Approach
To address these challenges, researchers at the Chinese Academy of Sciences have proposed an innovative selection method called ID-SELEX (Identification by Selection and Enrichment of Aptamers). This approach includes a molecular identification marker, which labels each RNA template with a unique molecular identifier (UMI).
This UMI labeling is crucial because it helps reduce biases that can arise during multiple rounds of amplification by polymerase chain reaction (PCR). PCR is a common technique used to make millions of copies of a specific DNA or RNA sequence, but it can sometimes introduce errors or skew results. By using UMIs, scientists can ensure that they accurately identify aptamer candidates without the interference of these biases.
Rapid Screening with ID-SELEX
The effectiveness of the ID-SELEX method has been demonstrated through its successful application in identifying high-quality RNA aptamers targeting the human colon cancer cell line HCT-8. Remarkably, this identification was achieved in just two rounds of selection. Furthermore, the versatility of ID-SELEX was showcased when the researchers selected six RNA aptamers targeting the mouse myoblast cell line C2C12 in only one round of selection.
The Role of RNA Sequencing
A critical aspect of the ID-SELEX method is its reliance on high-throughput sequencing, a powerful technology that allows scientists to read and analyze large amounts of RNA sequences quickly. RNA sequencing provides detailed information about the RNA molecules present in a sample, enabling researchers to identify which aptamers bind effectively to their targets. This ability to rapidly analyze RNA sequences is essential for the efficient discovery of new aptamers, significantly speeding up the research process.
Implications for Biomedical Research
The potential applications of ID-SELEX and RNA aptamers are vast. By enabling faster and more efficient aptamer discovery, this method paves the way for advancements in biomedical research, clinical applications, and precision medicine. RNA aptamers could be used to create targeted drug delivery systems, improve imaging techniques in cell biology, and develop new therapeutics that specifically address various diseases.
The innovative ID-SELEX method, combined with the power of RNA sequencing, represents a significant step forward in the field of molecular biology. It not only streamlines the process of selecting RNA aptamers but also opens up new possibilities for their use in understanding and treating complex diseases. As research continues, the development of RNA aptamers could lead to more personalized and effective medical treatments, marking a promising advancement in precision medicine.
