Yes, I said crackpipe.
Why? Because when a crackhead takes one suck from the pipe, it takes two back. The addict gets something from it, but they lose way more than they gain.
For me, social media is that crackpipe, and I am that crackhead.
Social media promised us so much. We could share ideas, thoughts, and information and stay connected to the people that matter. But as the Social Media monster grew, it became something far darker.
Here are 10 (science-backed) reasons I’m ditching the digital crack for good.
#1 – You’re Addicted & It’s Killing You
Addiction is when you can’t control your use, and you continue using despite the harm it causes.
By that definition, we’re all addicted to social media, and it’s a real problem.
You might think I’m being dramatic and say, “Surely the government would tell us if it was a problem, Skye?”
Well, those same governments once told us:
Smoking is good for you…


You should wrap babies in cellophane…


And to give babies 7-up…


Here’s the shocking truth:
While these studies focus on young people (as they’re the heaviest users), it’s important to remember these young people are the adults of the future.
The indicators of what’s coming are clear to see.
#2 – Likes = Self Worth?
The people we look up to influence what we feel is important.
In the past, we looked up to men and women doing great things. Today, we give our attention to whoever is the most outrageous.
Martin Luther King has been replaced by Mark from Love Island.
Social Media Influencers have become the stars of today, and likes are the currency.
And so we equate our value to how many likes we get.
Our drive for external validation and approval is so deep, we perform our own brand of superficial and attention-seeking behaviours in the hope of “going viral.”
We try to fit in with what’s popular, even if it’s not who we are.
We’re jumping through hoops to get the bone.


Looking Outside yourself for direction is normal; we came from tribes, after all. But basing your identity on what people on the internet think is crazy.
You try to live up to the lifestyle of the influencers and find it only brings anxiety and depression.
Your idea of their “perfect life” isn’t even real.

Forget what the world tells you to be, do the things that move you.
The secret to everything is being yourself.
Tension is who you think you should be; relaxation is who you are.
Ancient Chinese proverb
#3 – Your Return On Investment is Negative
What do you get out of social media?
- A couple of good memes
- DM’s from your friends and family
- Stay on top of the news
- Find places you’d like to travel to
Now consider this: What does it take back from you?
You already know you could do so much with your hours of mindless scrolling, so why do you do it?
It’s because of FOMO (fear of missing out).
You’re constantly in a state of worry about missing that picture or event that everyone else is talking about.
Here’s the kicker, though…
You’re missing out on your life.
You could be doing something creative and fulfilling, building a life beyond what you ever thought possible.
If you want to do something with your life, why spend 2-6 hours a day on something proven to make it worse?
#4 – With So Much Noise, How Can You Hear Yourself?
Want to know why you always feel so rushed, even on your days off?
Here’s what the average person’s day looks like:
You are being overwhelmed by messages, requests, and information. Many are telling you who you are and what you should be.
With so much noise, how can you hear yourself? Where’s your dialogue with yourself?
Your intuition needs space to communicate with you.
Social media opens the door to opinions on a scale we’ve never seen before.
Everyone has a voice.
While that’s good, the downside is that many use that voice to parrot “official narratives” or whatever conspiracy feels right to them instead of thinking for themselves.
In our overwhelming digital world, we often go with the majority, adopting the opinions of others to save time.
This “quick reference” process is efficient, but it’s not effective. When was the last time you asked yourself, “What do I really think?”.
The innovations that pushed society forward have come from freethinkers.
So I believe creating the space to think for yourself will make you highly valuable in a world of distracted, “me too” merchants.
#5 – Social Media Robs The Joy From Your Moments
Do you remember the days before you had a camera phone?
- You’d be at the Eiffel Tower having a blast snapping pictures and savouring the moment.
- You’d marvel at the splendour and imagine the people walking the same steps a hundred years before you.
- You’d get home, and weeks later, your pictures would be developed, and only then would you see how you looked.
- You’d show the photos to your family and maybe some friends, but probably no more than 20 people saw them.
Outcome: You experienced the moment fully.
Today, instead of marvelling at the monument, we’ve found ourselves doing this:
- Planning outfits weeks in advance to ensure we coordinate
- Posture, pose, and try to look like you’re having fun (even if you’re not)
- Run over to the camera to hyper-critically judge how you look after every 5 clicks
- Spend hours editing your pics for the perfect Instagram post
Outcome: The process of chasing the perfect shot sucks the joy from the moment. You miss the whole experience.
An experience that you could have cherished forever is gone. Traded for an anxiety-producing flurry of photos and a quick dopamine fix for the few minutes after you finally post the (heavily edited) picture.
Doesn’t that sound messed up when you read it back?
The need to be perfect and receive validation from your followers makes you wonder who you’re living for.
#6 – You’re Connected to Everyone, Yet Connected To No One
You’re probably living an increasingly isolated life.
Just you and the few friends and family you see in person. If you’re like most people, the only way you connect to the world beyond that is through your phone.
The internet gave us connection on a broader scale than ever, yet the depth of connection is missing.
Even with our families and friends, we’ve started to say “follow my Instagram” as a replacement for quality time.
I’m guilty of this. I’d tell my family the same and to subscribe to my newsletter. They did, but they wanted some real time with me, not the polished version they could see through.
Nobody wants the PR version of you. The carefully crafted message and polished image you cut, curate, and distribute far and wide.
Everyone sees it, but nobody feels it. The real you is missing. The vulnerability, the spectrum of emotions, and even the quirks you don’t like about yourself (that everyone else loves).
There is no substitute for real, personal connection.
Our families and friends deserve better, and I’ve committed to talking to them more often and visiting them whenever possible.
#7 – Is It Really Worth Losing Sleep Over?
Not getting enough sleep causes severe problems like depression, brain fog, anxiety, hostility, and even psychotic disorders.
These shocking facts give you an idea of just how crucial sleep is to our general well-being:
Unfortunately, the internet and sleep don’t go very well together.
This study claims 57% of teens who use technology in their bedrooms suffer from some form of sleep disruption.
The blue light emitted from your screen gives your brain the signal to stay alert when you should be winding down.
Even if you don’t delete social media, putting your devices away an hour before bedtime will help you sleep better and wake up refreshed.
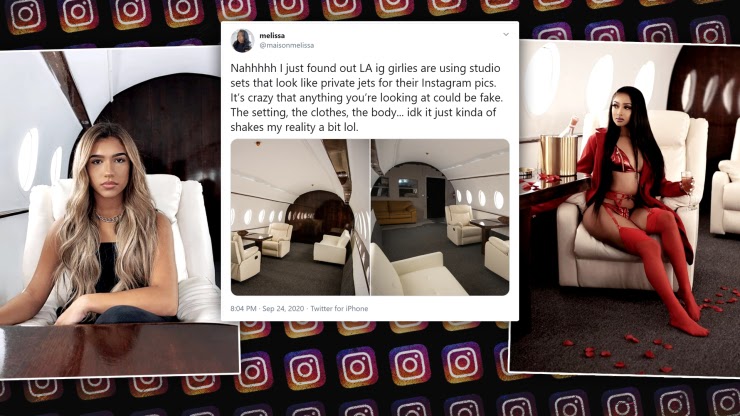
#8 – What You See Is Not What You Get
Social media makes you think everyone else is living a perfect life.
Travelling to exotic places, looking like a million bucks, and enjoying life to the fullest.
You forget that you’re comparing your life to someone else’s heavily filtered and edited version of reality.
It’s such a problem that there’s a new disorder called ‘Snapchat Dysmorphia,’ which is causing concern for plastic surgeons. Instead of wanting to look like Brad Pitt or Jennifer Aniston, people now want to look like software edited versions of themselves with perfect bodies and a flawless smile.
Chasing a digital avatar of yourself (which is not physically possible to become) destroys your self-esteem and your individuality.
The unique aspects of you make you interesting, endearing, and, yes, even attractive.
How can you stand out if you’re a clone?
#9 – Big Tech is in Control, and It’s Disturbing
If the platform is free, you are the product.
The social media apps are not free, data is the new oil, and big tech companies have mastered the art of collecting your data and selling it.
Ever searched for something and soon got flooded with ads and offers for that exact product?
That’s the power of your data being used to direct your attention so they can monetise you.
“Our attention can be mined. We are more profitable to a corporation if we’re spending time staring at a screen, staring at an ad, than if we’re spending that time living our life in a rich way. And so, we’re seeing the results of that. We’re seeing corporations using powerful artificial intelligence to outsmart us and figure out how to pull our attention toward the things they want us to look at, rather than the things that are most consistent with our goals and our values and our lives.”
Justin Rosenstein, Co-Founder of Asana
When the platform directs your attention that much, how free are you?
With that power, Big Tech has also started to direct conversations. Censoring views that don’t agree with the mainstream narrative, even if there is evidence to suggest they’re more than mere conspiracies.
Yet, those same companies don’t censor some of the most disturbing content that everyone with a brain agrees should be banned, like Twitter letting paedophiles publicly discuss their sexual attraction to minors.
With the power they have, they focus on monetising and censoring over protecting society’s most vulnerable people, and that leaves a bad taste in my mouth.
What Now?
The internet has made life better for so many of us, myself included. It’s easier than ever to stay connected to the people we love, even if they’re halfway across the world.
But when you assess the cost of social media, it’s clear it’s taking more from you than it’s giving you.
Remember, all technology has an off switch.
Your life is your own, and whether or not you’re ready to get off the carousel yet, unplug from time to time. Doing so allows you to genuinely choose when and how you want to use social media to reinforce your values and beliefs.
I leave you with this to think about:
“Privacy is the fountainhead of all other rights. Freedom of speech doesn’t have a lot of meaning if you can’t have a quiet space. A space within yourself, within your mind, within the community of your friends, within your home, to decide what it is you actually want to say.”
Edward Snowden
