RNA sequencing (RNA-seq) has opened up new frontiers in understanding gene activity and its role in health and disease. However, when researchers work with sensitive patient data—especially data collected from multiple institutions—sharing and combining information becomes a tricky balancing act. On one hand, pooling data can lead to deeper insights and more robust statistical analyses. On the other, privacy concerns and regulations can restrict the sharing of raw data across institutions, creating “data silos.” This challenge has been a significant barrier to large-scale transcriptome studies.
The Promise of Federated Learning
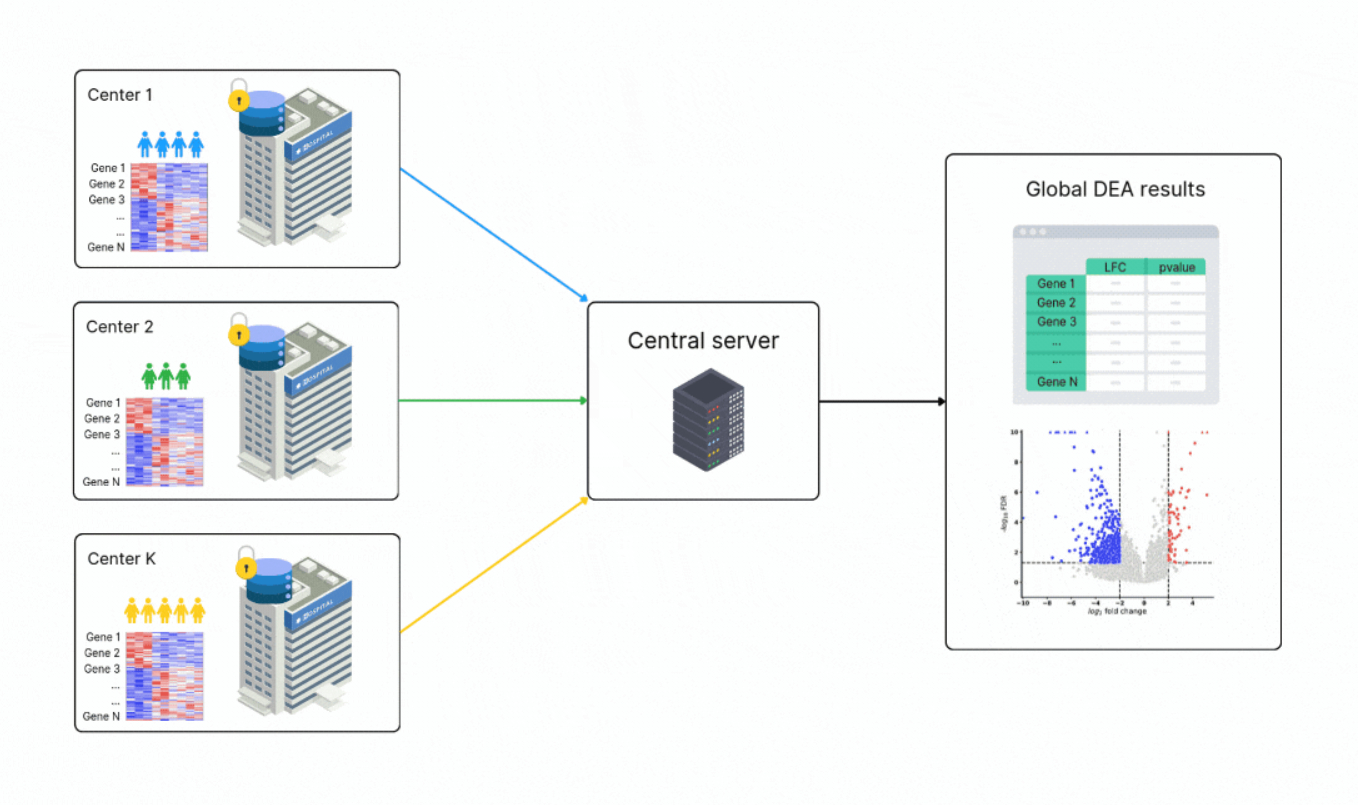
A new approach called federated learning (FL) offers a solution to this problem. Federated learning allows researchers to train computational models on data from multiple sources without requiring the raw data to leave its original location. Instead of moving data, institutions share only the results of their local analyses, ensuring privacy while enabling collaboration.
Building on this approach, scientists at Owkin recently developed FedPyDESeq2, a software tool specifically designed for differential expression analysis (DEA) of RNA-seq data stored in silos. DEA is a common method used to identify which genes are more or less active under specific conditions, such as comparing tumor and healthy tissues.
What Makes FedPyDESeq2 Special?
FedPyDESeq2 adapts the popular DESeq2 pipeline—a trusted tool for RNA-seq analysis—to work in federated environments. By combining the strengths of DESeq2 with privacy-preserving FL techniques, FedPyDESeq2 allows researchers to analyze siloed datasets as if they were pooled together, all without compromising data security.
To test how well it works, the researchers applied FedPyDESeq2 to RNA-seq data from The Cancer Genome Atlas, focusing on samples split across geographical regions. The results were impressive:
- Accuracy: FedPyDESeq2 achieved results nearly identical to running DESeq2 on a fully combined dataset.
- Performance: It significantly outperformed traditional meta-analysis methods, which tend to lose statistical power in complex or varied datasets.
Why This Is Important
FedPyDESeq2 is a game-changer for RNA-seq research in several ways:
- Enhanced Collaboration: Institutions can now collaborate on transcriptome studies without needing to share sensitive raw data, paving the way for larger and more inclusive studies.
- Improved Insights: By maintaining high statistical power, researchers can extract deeper biological insights even in diverse or fragmented datasets.
- Privacy Protection: FedPyDESeq2 ensures compliance with strict privacy regulations while enabling cutting-edge analysis.
The Road Ahead
As privacy concerns grow and data-sharing rules tighten, tools like FedPyDESeq2 will become increasingly valuable. They represent a step toward unlocking the full potential of RNA-seq data while respecting the privacy and security of individuals. By bridging the gap between collaboration and confidentiality, FedPyDESeq2 sets a promising precedent for future innovations in computational biology.
